asmjit::x86::Vec Class Reference [¶]
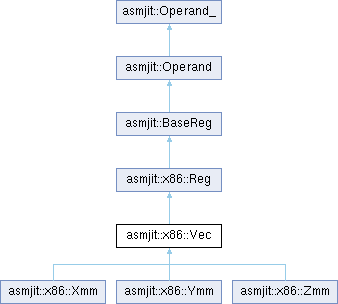
Vector register (XMM|YMM|ZMM) (X86|X86_64).
To get a specific register you can use:
- specific registers directly, like
x86::xmm0orx86::ymm1,x86::zmm2, etc... - construct a register operand dynamically, like
x86::xmm(id),x86::ymm(id), andx86::zmm(id) - use
Vec::make_v[128|256|512](id)orVec::make_[xmm|ymm|zmm](id)API for convenience
To cast a register to a specific type, use Vec::v128(), Vec::v256(), Vec::v512(), Vec::xmm(), Vec::ymm(), and Vec::zmm() member functions. Each cast first clones the register and then changes its signature to match the register it has been casted to.